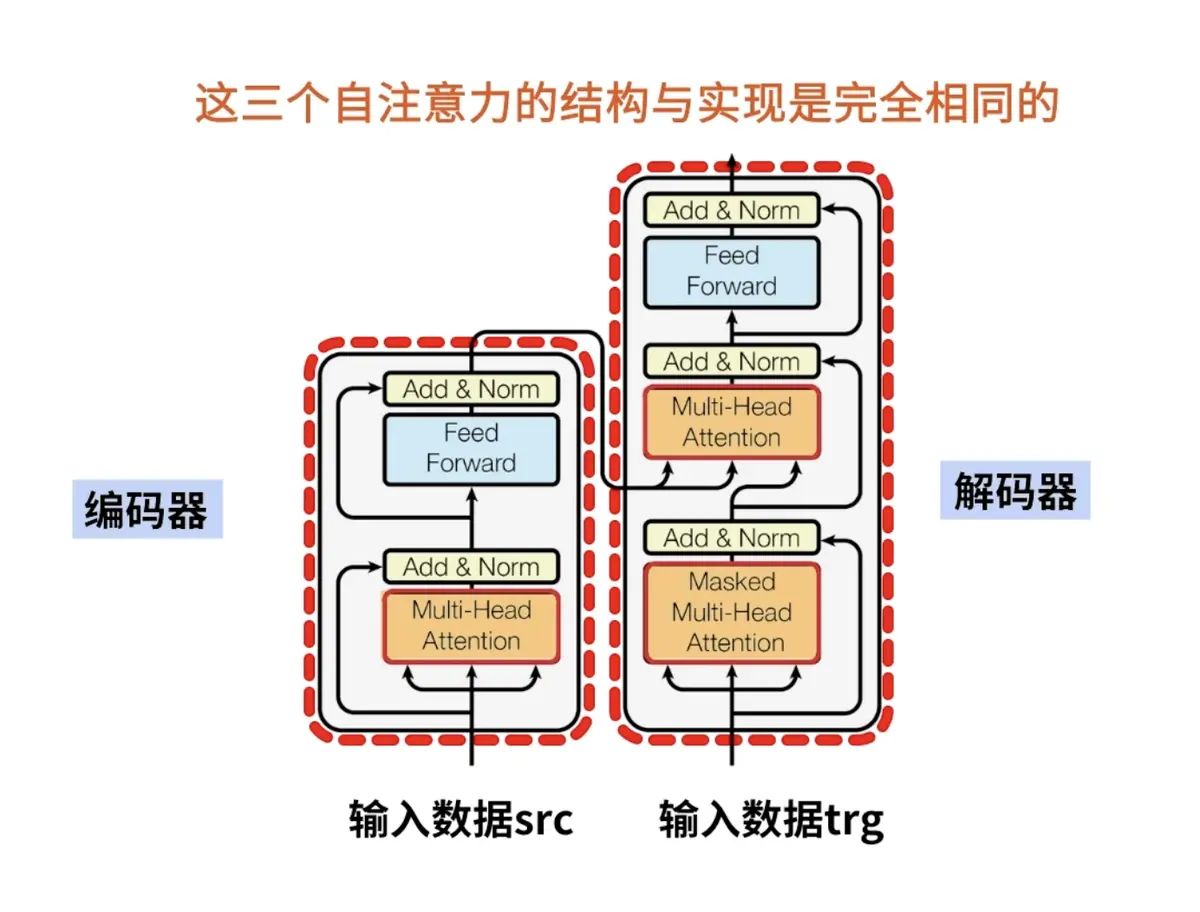
知识概念
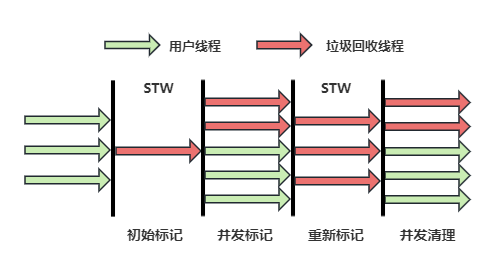
CMS垃圾回收
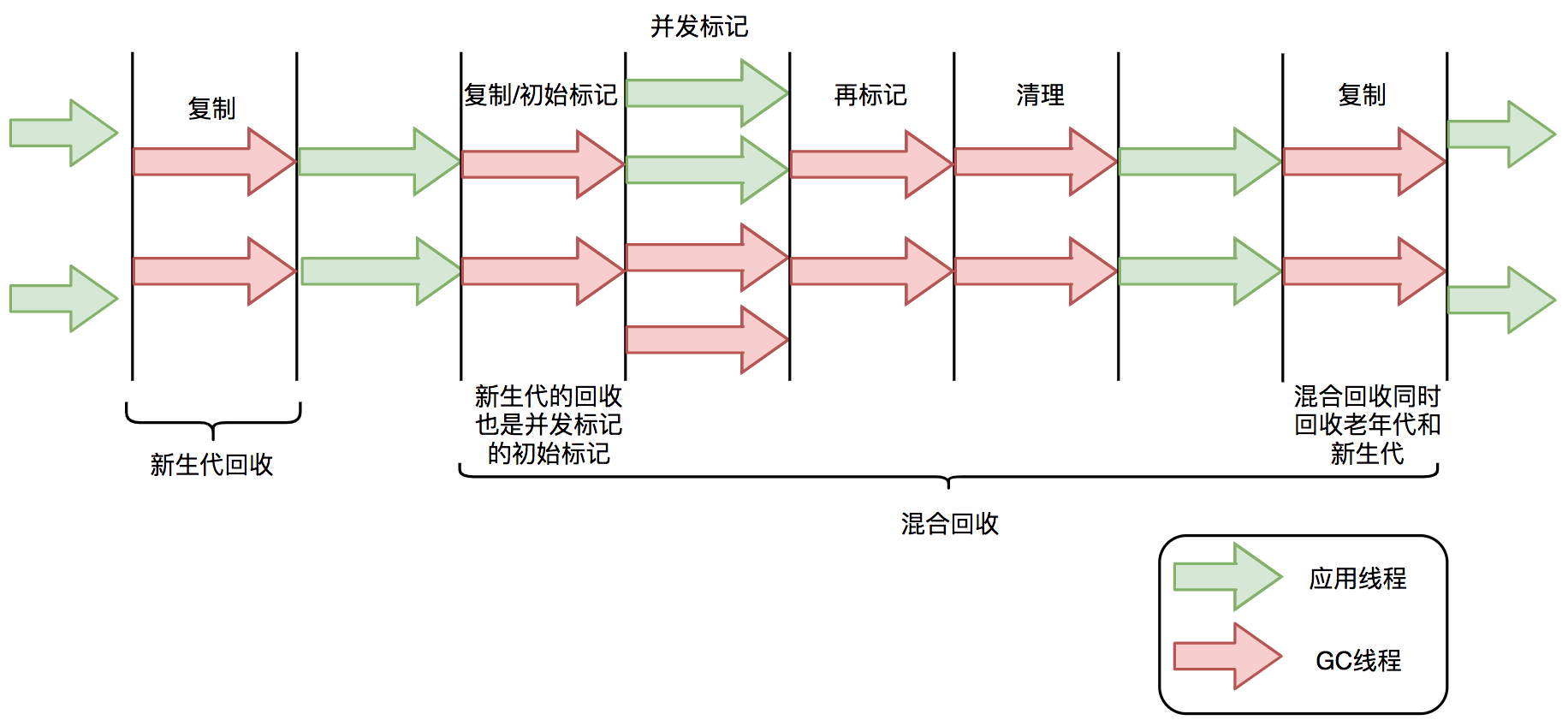
回收步骤:
年轻代使用复制算法,老年代使用标记-清除算法。
老年代GC触发条件:CMS 不会等到老年代完全满了才进行回收,而是当老年代使用达到一定阈值时(默认 92%)开始回收,以避免长时间的 Full GC。
标记策略 - 增量更新
在并发标记过程中,当发现一个原本未被标记为存活的对象,因为某个应用程序线程执行了写操作而使得其被一个已标记的存活对象引用时,并不会立即将这个原本未标记的对象标记为存活,而是将这个引用关系变化记录下来,等待重新标记阶段再根据这些记录来更新标记情况,确保该对象能被正确标记为存活。
- CMS使用插入写屏障
新增黑色到白色的引用,JVM就会通过写屏障,将黑色变成灰色
- CMS 也有卡表
在CMS中,写屏障主要用于记录跨代引用(即老年代对象引用新生代对象或反之)的变化,并将这些变化信息反映到卡表中。
卡表本质是bit数组,帮助定位需要重新扫描的老年代区域。
CMS缺点:
内存碎片问题:由于 CMS 是标记-清除回收器,不会整理内存,老年代内存中会产生碎片,这可能导致 Full GC。
并发模式失败:如果老年代在回收过程中无法及时腾出足够空间,可能会发生“Concurrent Mode Failure”,这会退回到单线程的 Serial Old GC,导致长时间暂停。
较高 CPU 消耗:CMS 在回收时需要额外的 CPU 资源,可能对 CPU 密集型应用有较大影响。
浮动垃圾:CMS垃圾回收器在并发标记和并发清理阶段由于用户线程并未停止,该阶段可能会产生浮动垃圾,无法在本次被回收,只能等到下一次垃圾回收。
G1(Garbage First GC)
参考链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/RqLSu8VNcvQRMh0D-QA9Bw
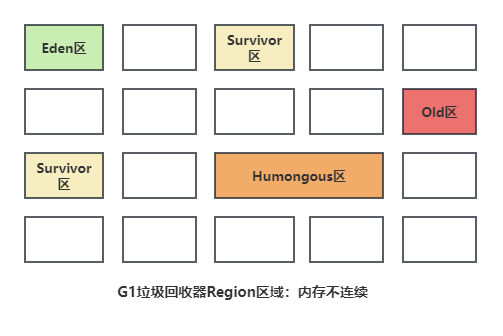
分区堆模型:G1 将堆分成多个大小相等的区域(Region),不同区域可能属于年轻代或老年代。通过收集垃圾最多的区域进行复制回收,因此称为“Garbage First”。
混合回收:G1 能够同时回收年轻代和老年代的内存,避免了 Full GC 的大范围内存整理。
暂停时间可控:G1 可以根据设置的最大暂停时间目标(默认 200ms),智能选择要回收的区域,来控制 GC 的影响。
生产环境中,G1 最稳定的堆内存范围是8GB ~ 128GB;少数优化到位的场景(如高 CPU 核心、低对象分配速率)可到 256GB,但超过 256GB 后,G1 很难维持低延迟
区块划分
Eden区、Survivor区、Old区和Humongous区(存放大对象,老年代的一部分)
区域Region的内存大小默认是通过整个堆内存大小除以2048得到的,例如整个堆内存为4G,则Region = 4G / 2048 = 2M,同时也支持通过JVM参数指定Region的内存大小。
阶段划分
- 年轻代回收(Young GC)阶段:
当Eden区被填满或者达到了某个条件(例如,G1认为回收这些区域的收益较高)时,就会触发一次年轻代回收。
年轻代回收的过程中,存活的对象会从Eden区和Survivor区复制到另一个Survivor区或者直接晋升到老年代。
这个过程通常是Stop-The-World(STW)的,即在回收过程中,应用程序的其他线程会被暂停。
- 混合回收(Mixed GC)阶段:
当老年代的占用率达到了一定阈值(由-XX:InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent参数控制,默认值为45%),G1会启动混合回收阶段。
在这个阶段,G1不仅回收年轻代,还会回收一部分老年代的区域,这些区域被认为含有较多垃圾。
混合回收也是STW的,但G1会尝试在用户指定的停顿时间目标内完成。
回收技术
G1垃圾回收器年轻代回收时,采用了三种关键技术,分别是记忆集、卡表和写屏障。
如果年轻代的对象被老年代的对象引用了,应该如何识别出来呢?
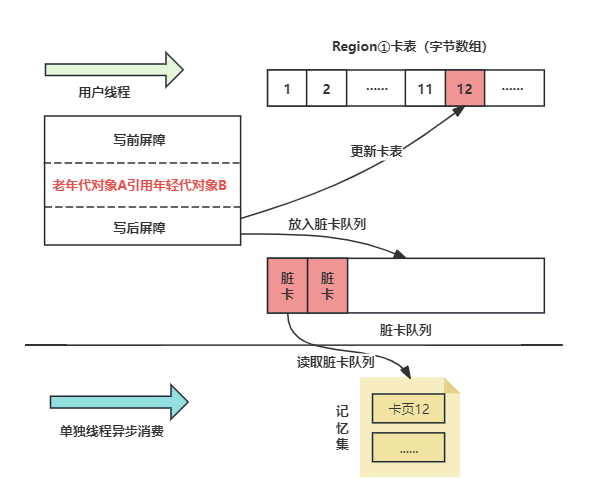
- 记忆集和卡表实现
当某个卡页中的对象引用自己Region区域的对象时,会将老年代的卡表对应编号位置的字节修改为1,为1的字节被称之为脏卡。
在Young GC回收年轻代对象时,会将记忆集中的对象也加入到GC Root中,有效避免年轻代的对象被错误的回收。
- G1卡表和CMS卡表有啥区别?
G1卡表维护范围:覆盖整个堆(包括年轻代和老年代分区)。CMS只是老年代。
G1卡表维护信息:对每张卡,不仅标记是否脏,还关联对应的 Region 信息,方便定位影响的区域。
- SATB:
核心思想是:在标记过程的起始阶段捕捉一个对象的快照,并基于这个快照来进行后续的标记工作。
在标记阶段开始时,G1垃圾收集器会创建一个当前所有对象的快照。
在这个快照之后新生成的对象,由于它们尚未被任何旧对象引用,因此它们会被直接标记为黑色,表示它们是活跃的,不应该被回收。
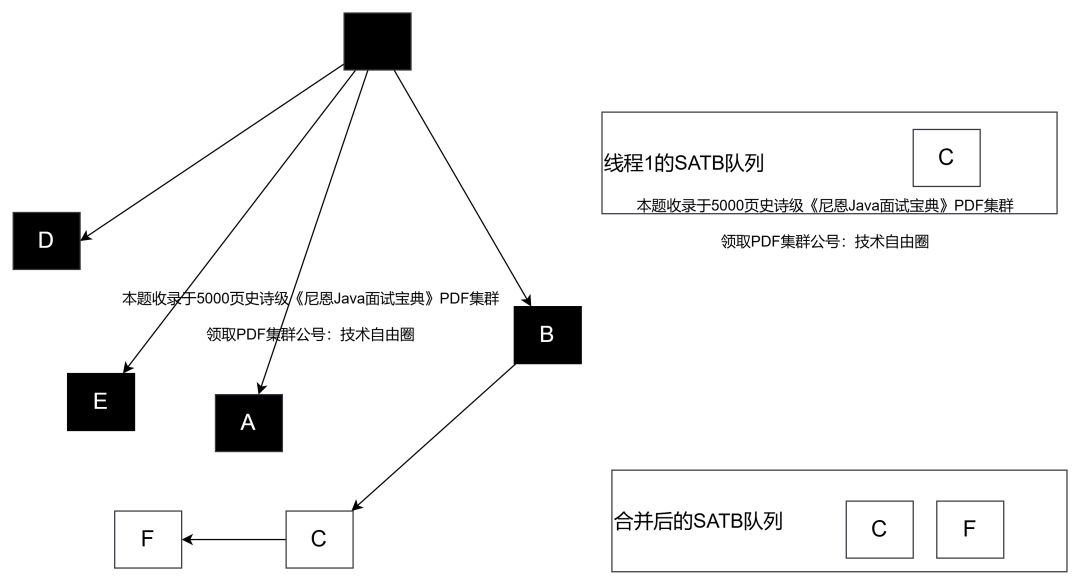
为了处理在标记过程中可能发生的对象引用变化,G1采用了前置写屏障技术。
前置写屏障技术 会在引用赋值操作(如B.c = null)之前被触发,将即将被改变引用的对象(在这个例子中是C)放入SATB待处理队列中。
每个线程都有自己的SATB队列,但最终这些队列会被汇总到一个全局的SATB队列中。
- 写屏障:
更新卡表状态的底层采用了写屏障技术(具体为写后屏障),当执行对象引用相关的代码时,会在其代码前后插入对应的指令,判断到老年代对象引用年轻代对象时,会更改卡表中对应的字节为脏卡,同时会将脏卡放入到一个脏卡队列中,JVM会通过单独的线程,定期读取脏卡队列中的数据,更新记忆集。
优点:
适用于大堆内存:G1 尤其适合大堆内存(通常超过 6GB)环境,能够有效处理较大的老年代回收。
避免 Full GC:通过区域化内存管理和并行收集,G1 几乎避免了传统的 Full GC 停顿。
碎片整理:G1 在回收时会进行内存整理,减少了内存碎片问题。
提前触发回收(少量多次),每次垃圾回收时间短。
- 浮动垃圾:SATB基于初始快照进行标记,因此在本轮垃圾回收过程中,可能会将一些实际上应该被回收的不存活对象错误地标记为存活对象。这些错误标记的对象被称为“浮动垃圾”。这些浮动垃圾只能下一次的时候回收。
问题排查:G1在执行Full GC时,会在GC日志中记录相关信息,如[Full GC (Allocation Failure)],表示由于分配失败触发了Full GC。
怎么实现的预测回收STW?
如果目标延迟是 50ms,G1 会计算 “回收多少个 Region 能在 50ms 内完成”,只回收这部分,剩下的留到下一次 GC 处理。
如果某次 GC 实际停顿超过了目标值,模型会在下一次自动减少回收的 Region 数量;如果远低于目标值,会适当增加,平衡延迟和吞吐量。
ZGC
超低延迟:ZGC 是一种面向超低延迟设计的垃圾回收器,旨在将垃圾回收停顿时间控制在 10ms 以内。
堆内存极大:ZGC 支持非常大的堆内存(TB 级别),这使得它在处理大规模内存应用时有很大的优势。
1.着色指针(Colored Pointers)
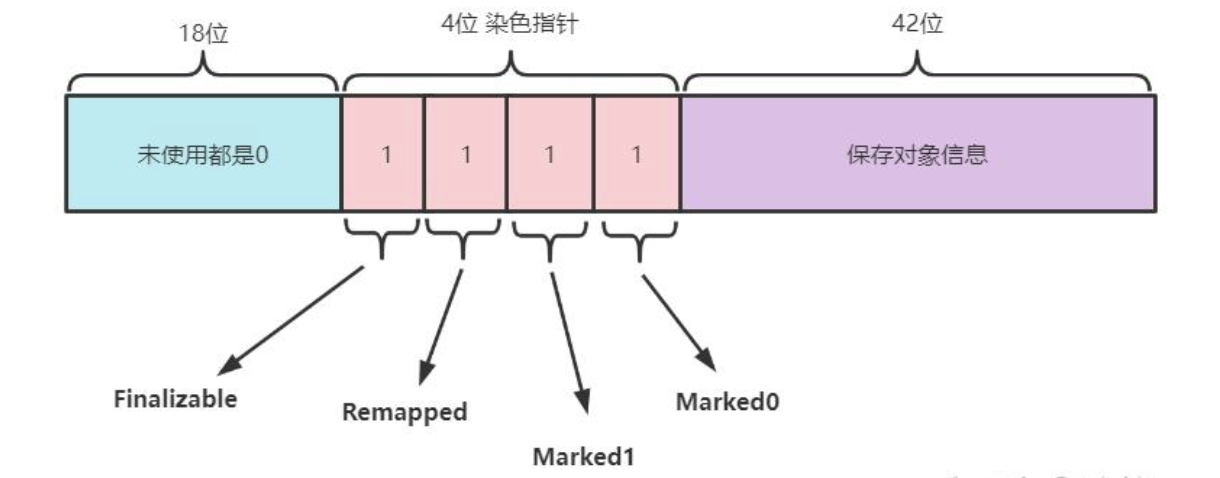
原理:利用 64 位指针的高几位空闲位(不同 CPU 架构空闲位不同,如 x86-64 保留 18 位)存储标记信息,包括:高18位都是0暂未使用,剩余的46位实际上是能支持64TB的内存的,但是目前来说计算机内存空间还没这么大。剩余的46位中,高4位用来保存了4个标志位,低42位置才是用来保存对象的指针,所以ZGC最大可以管理的内存不超过4TB。
Marked0/Marked1:三色标记对象是否存活(用于并发标记);
Remapped:标记对象是否已完成重定位(用于并发重定位)。
Finalizable:是否需要通过 finalize 方法来访问到(Finalizable)等信息。
优势:
无需修改对象头,减少内存占用;
指针本身携带状态,GC 阶段无需扫描整个堆,大幅提升效率;
支持并发重定位(对象移动时,应用线程可同时访问旧指针,由读屏障透明转发到新地址)。
2.读屏障(Load Barrier)
ZGC 仅在应用线程读取对象指针时插入读屏障,核心作用是:
指针验证:检查指针的标记位是否合法;
指针转发:若对象已被移动,自动将旧指针转发到新地址;
并发标记辅助:在标记阶段,协助标记对象的可达性。
读屏障的性能开销极低(实测约 1%~3%),远小于传统 GC 的写屏障。
在从堆读取引用时介入:1
Object o = obj.fieldA; // 触发读屏障
当对象被移动时,屏障自动修正指针,实现指针自愈。
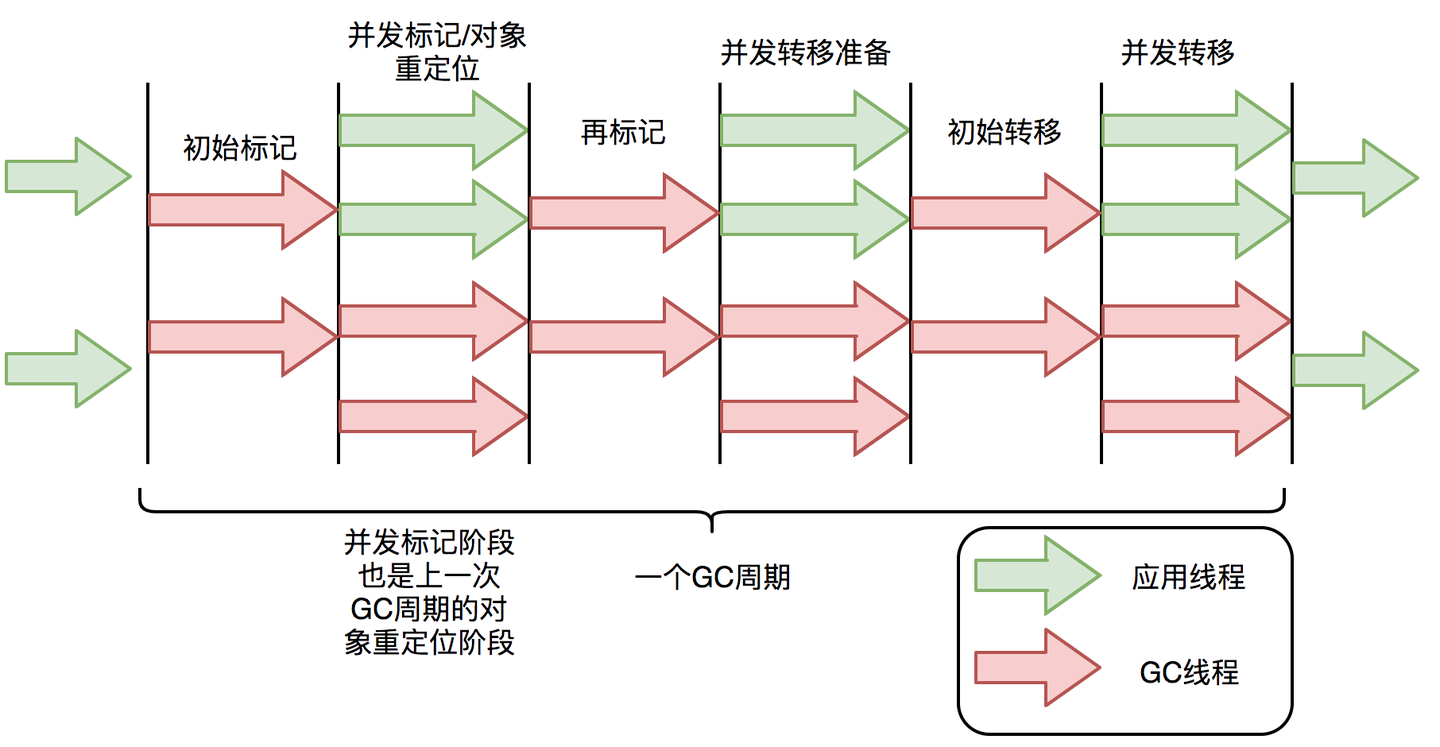
- 回收流程
1.初始标记(Initial Mark)- STW
目标:标记 GC Root 直接引用的对象。
特点:停顿时间微秒级,几乎可以忽略,通常与线程的 safepoint 重合。
2.并发标记(Concurrent Mark)- 并发
目标:从初始标记的对象出发,遍历整个对象图,标记所有存活对象(通过着色指针的 Marked0/Marked1 位)。
特点:与应用线程并发执行,无停顿;标记过程中,新分配的对象自动标记为存活。
3.重定位(Relocation)- 并发 + 极短 STW
这是 ZGC 实现低延迟的核心阶段,分为三步:
重定位选择(Concurrent Relocation Selection):并发选择需要回收的 Region(垃圾比例高的 Region);
重定位准备(Concurrent Relocation Preparation):准备重定位的 Region,标记为 “正在重定位”;
并发重定位(Concurrent Relocation):将存活对象移动到新的 Region,同时通过读屏障让应用线程透明访问新地址;
最终重定位(Final Relocation):极短 STW,处理极少数未转发的旧指针。
4.并发重映射(Concurrent Remap)- 并发
目标:更新应用线程中所有指向旧 Region 的指针,使其直接指向新地址,消除读屏障的转发开销。
特点:与应用线程并发执行,优先级较低,可被 GC 周期打断(下次 GC 继续处理)。
本质还是标记-复制
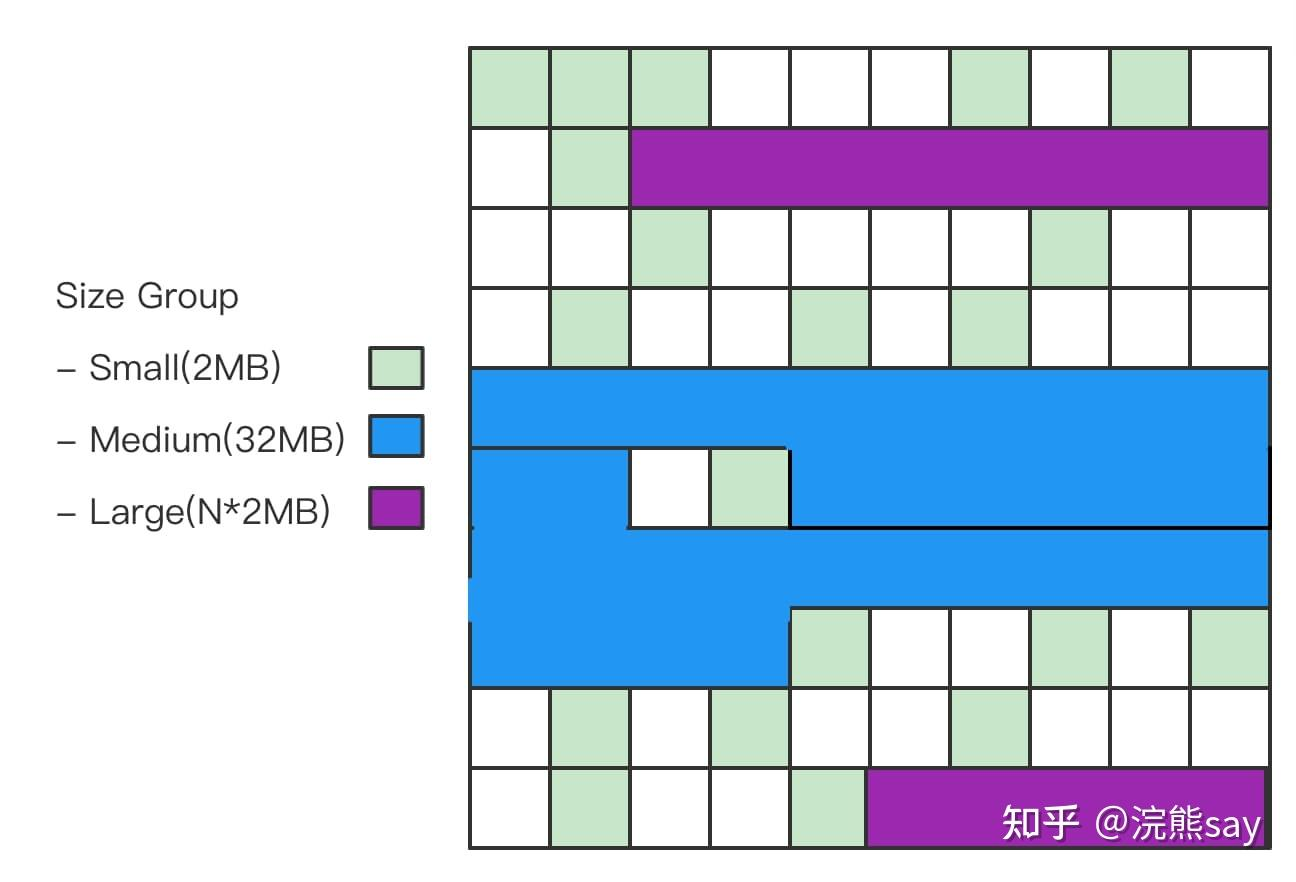
- 动态的区域容量大小:
ZGC引入了不同大小的Region,包括Small Region(2MB)、Medium Region(32MB)和Large Region(可变大小),使得ZGC在内存分配时能够更好地适应不同大小的对象,提高内存利用率。
- ZGC主要问题
浮动垃圾:无分代导致全堆扫描,新对象需下次GC回收
内存开销:颜色指针和读屏障带来额外开销
三色标级
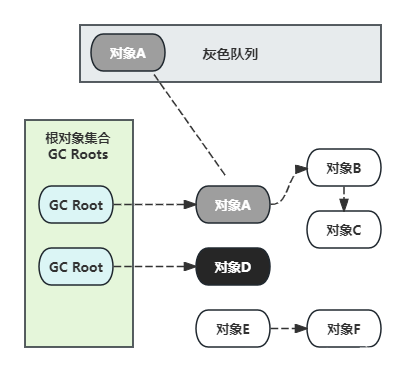
CMS和G1都有三色标记算法。标记对象的颜色其实是通过位图(bitmap)实现的,默认的白色对象的bit为0,黑色对象的bit位会被设置为1,而灰色对象不会体现在位图,会被放置于一个单独的队列
面试
Full GC
1. 老年代空间不足
这是最常见的触发原因:
新生代对象经过 Minor GC 后,存活对象需要晋升到老年代,但老年代剩余空间不足以容纳这些对象。
大对象直接分配到老年代时,老年代空间不足(大对象指需要连续内存的对象,如大数组、大字符串)。
老年代中内存碎片过多,虽然总空间足够,但没有连续的内存块容纳新的大对象(CMS 收集器尤为明显)。
2. 永久代 / 元空间(Metaspace)不足
JDK 7 及之前:永久代(PermGen)存储类元数据、常量池等,当永久代空间不足时,会触发 Full GC 尝试回收无用的类信息(如卸载不再使用的类),若回收后仍不足则抛出OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space。
JDK 8 及之后:永久代被元空间(Metaspace)取代,元空间默认使用本地内存,但如果设置了-XX:MaxMetaspaceSize且达到上限,也会触发 Full GC 尝试卸载类,失败则抛出OutOfMemoryError: Metaspace。
3. CMS 收集器的特殊触发场景
CMS(Concurrent Mark Sweep)是老年代并发收集器,除了老年代不足外,还有专属触发条件:
CMS Concurrent Mode Failure:CMS 在并发标记 / 清理阶段,老年代空间被新对象占满,无法继续并发回收,会触发 “Concurrent Mode Failure”,进而强制触发 Full GC(通常会退化为 Serial Old 收集器,停顿时间更长)。
CMS 晋升失败(Promotion Failure):新生代 Minor GC 时,存活对象要晋升到老年代,但老年代空间不足,且 CMS 无法及时腾出空间,触发 Full GC。
显式设置-XX:CMSFullGCsBeforeCompaction:指定 CMS 执行 N 次 Full GC 后,触发一次内存碎片整理(Serial Old),这也是 Full GC 的一种。
4. 显式调用 System.gc ()
代码中调用System.gc()或Runtime.getRuntime().gc()时,JVM可能触发 Full GC(注意:这只是建议,JVM 可通过-XX:+DisableExplicitGC参数禁用该行为)。
常见场景:一些第三方库、框架(如 NIO 的 DirectByteBuffer 回收)可能会调用该方法,导致非预期的 Full GC。
5. G1 收集器的 Full GC 触发
G1(Garbage-First)作为混合收集器,触发 Full GC 的场景包括:
老年代达到-XX:InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent(默认 45%)阈值,且并发回收无法及时释放空间。
新生代晋升失败、大对象分配失败,且 G1 的混合回收来不及处理。
G1 的回收过程中,记忆集(Remembered Set)维护异常,也可能触发 Full GC。
6. 其他特殊场景
JVM 在做堆内存快照(如 jmap dump)时,可能会触发 Full GC 以获取一致性的内存快照。
某些 JVM 参数配置不当(如新生代 / 老年代比例不合理),也可能间接导致频繁 Full GC。
怎么定位?
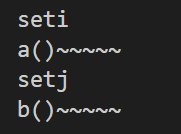
查看 GC 日志:添加 JVM 参数打印详细 GC 日志,关键参数:1
-XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCDateStamps -Xloggc:/path/to/gc.log
日志中会包含Full GC关键字,以及触发原因(如Allocation Failure、Metadata GC Threshold等)。
使用工具分析:
jstat:jstat -gcutil
jvisualvm/JMC:可视化监控 GC 状态,定位 Full GC 触发时机。
CMS vs G1
1.堆内存管理:连续分区(G1) vs 离散 Region(CMS)
G1 可以动态调整年轻代 Region 的数量,回收时只挑选 “垃圾多、回收性价比高” 的 Region,从根本上限制单次回收的范围。
2.延迟控制:被动并发 vs 主动预测
范围可控,有预测机制
3.标记清除(CMS) vs 标记复制(G1)
内存碎片
4.stw period
- G1
整个 Young GC 全程都是 STW 阶段,但因为只处理年轻代 Region,且多线程并行执行,耗时通常在 几毫秒~30 毫秒。
Full GC 会回收整个堆,全程 STW,秒级。